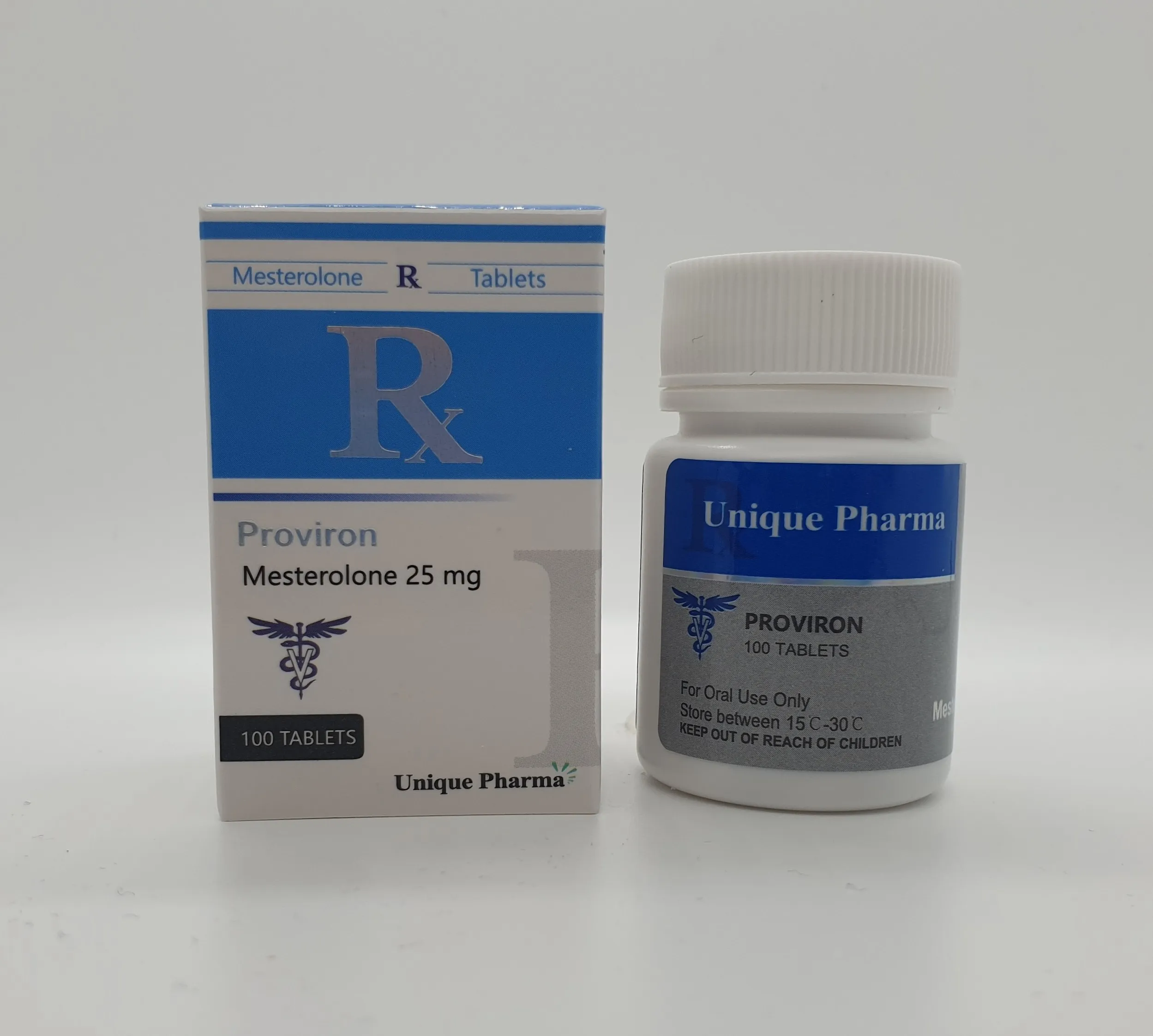
UNIQUE PHARMA QUALITY: Premium pharmaceutical grade Mesterolone (Proviron) manufactured under strict GMP conditions with 99.8% purity verification.
Proviron from Unique Pharma represents our commitment to delivering exceptional quality performance enhancement compounds. Each batch undergoes rigorous testing to ensure consistent potency and purity standards.
Key Characteristics of Proviron
This oral compound is administered via oral tablets and remains active in your system for approximately 12-13 Hours. Notable features include:
- Pharmaceutical grade manufacturing
- Batch-tested for purity and potency
- Consistent dosing per unit
- Optimal bioavailability
Primary Benefits:
- Enhanced performance and recovery
- Quality-assured formulation
- Reliable and consistent results
- Professional-grade compound
Mechanism of Action
Mesterolone works by interacting with androgen receptors in muscle tissue, promoting protein synthesis and nitrogen retention. This creates an optimal environment for muscle development and recovery. The compound's unique molecular structure provides specific benefits that distinguish it from other options in its class.
Usage Guidelines
Unique Pharma Proviron is suitable for experienced users who understand proper cycling protocols. Always consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any supplementation regimen. Proper post-cycle therapy should be considered based on individual needs and cycle duration.
Recommended Applications
This compound is commonly incorporated into both bulking and cutting protocols depending on the user's specific goals. Its versatility makes it a popular choice among athletes and bodybuilders seeking reliable results.
Potential Considerations
As with any performance compound, users should be aware of potential effects and monitor their response accordingly. Regular health monitoring is recommended during use. Individual responses may vary based on genetics, diet, training, and other factors.
Quality Assurance
Every Unique Pharma product undergoes comprehensive quality control including:
- Raw material verification
- In-process testing
- Final product analysis
- Stability testing
Warning: Keep out of reach of children. For adults only. Not intended for use by individuals under 18 years of age.
Related products
Other Unique Pharma products
1. Description — Clinical summary
Proviron is the trade name commonly used for mesterolone, an orally active androgenic compound derived from dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It is used clinically as an androgen replacement in men with symptomatic hypogonadism and has been used as adjunctive therapy in certain cases of male infertility and reduced libido. Mesterolone is primarily an androgen receptor agonist with relatively weak anabolic activity compared with testosterone. It is not aromatized to estrogens.
Key clinical points
- Active ingredient: mesterolone (commonly supplied as 25 mg tablets).
- Indications (examples): male hypogonadism (as androgen replacement), some off-label uses include treatment of decreased libido and male infertility in selected cases. Use and efficacy for infertility are variable and depend on underlying cause.
- Regulatory status: prescription-only in most jurisdictions. Use should be supervised by a clinician experienced in androgen therapy.
2. How does proviron work? — Mechanism of action
- Androgen receptor agonist: Mesterolone binds to androgen receptors in target tissues (muscle, liver, bone, central nervous system, prostate, skin), producing androgenic effects (virilization, libido enhancement) and limited anabolic actions.
- DHT derivative and non-aromatizing: Chemically related to DHT, mesterolone cannot be converted (aromatized) to estradiol, so it does not produce estrogen-mediated effects such as gynecomastia or water retention.
- Effect on sex-hormone binding globulin (SHBG): Mesterolone can decrease the binding of testosterone to SHBG (reported clinically), which may increase circulating free (biologically active) testosterone without increasing total testosterone concentrations.
- Hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis suppression: Like other exogenous androgens, mesterolone can suppress gonadotropin (LH/FSH) secretion at sufficient doses, which may reduce endogenous testosterone production and spermatogenesis over time.
- Pharmacokinetics (general): Orally active; hepatic metabolism; elimination half-life reported in clinical sources to be on the order of hours (frequent daily dosing may be used). Compared with 17α-alkylated oral androgens, mesterolone tends to have lower hepatotoxic potential, but liver monitoring is still prudent.
3. Dosage — Medical and varying usage guidelines
All dosing below is for information only. Use must be individualized and guided by a prescriber. Typical tablet strength is 25 mg.
Medical (approved and common therapeutic) dosing
- Male hypogonadism (adult men):
- Typical starting dose: 25 mg once to twice daily (25–50 mg/day).
- Some regimens use 25 mg two or three times daily (total 50–75 mg/day); total daily dose commonly ranges 50–100 mg in practice depending on response and tolerance.
- Duration: adjusted according to clinical response and biochemical monitoring; long-term therapy may be required for chronic hypogonadism.
- Male infertility / impaired sperm motility (off-label, selective cases):
- Doses commonly reported: 25–50 mg/day, often divided; treatment courses may run several months.
- Important: androgens can suppress spermatogenesis at higher doses; specialist consultation and careful semen monitoring are essential.
Special populations and cautions
- Women: Generally not recommended due to risk of virilization (voice deepening, hirsutism, menstrual irregularities). If considered (very rarely and under specialist guidance), doses must be very low and risk/benefit carefully weighed.
- Children/adolescents: Contraindicated except under specialist supervision because androgens can prematurely close epiphyses and impair growth.
- Elderly: Use caution with prostate disease or cardiovascular disease; start low and monitor carefully.
Dosing considerations
- Frequency: Because of relatively short elimination, many clinicians divide the daily dose (e.g., 25 mg two or three times daily) rather than giving it once daily.
- Combination therapy: Mesterolone should not be combined with other androgens or anabolic steroids without specialist oversight—additive suppression of the HPG axis and increased adverse effects can occur.
- Monitoring and adjustment: Dose adjustments guided by clinical response (symptoms, sexual function), laboratory tests (serum testosterone, LH/FSH), and adverse effects.
Overdose
- Management is supportive. No specific antidote. Stop the drug and provide symptomatic therapy and monitoring (hepatic function, electrolytes, cardiovascular status) as indicated.
4. Side effects — Common and rare adverse effects
Adverse effects are dose dependent. Many reflect androgenic activity.
Common and relatively frequent (may occur in ≥1% of users)
- Acne and oily skin
- Increased libido (or changes in sexual function)
- Increased facial/body hair or acceleration of male pattern hair growth
- Scalp hair loss in genetically susceptible individuals (androgenic alopecia)
- Mood changes (irritability, aggression, mood swings)
Less common / clinically important
- Suppression of HPG axis: decreased LH/FSH, suppression of endogenous testosterone production with long-term use; at higher doses this can reduce spermatogenesis and cause infertility or azoospermia
- Changes in lipid profile: reductions in HDL cholesterol and unfavorable changes in LDL; potential increase in cardiovascular risk factors with long-term use
- Prostatic effects: benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) exacerbation, increased prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
- Fluid retention is less common than with aromatizing androgens, but can occur
- Hepatic effects: mesterolone is generally less hepatotoxic than 17α-alkylated oral androgens, but elevated liver enzymes and rare cholestatic injury have been reported — monitor liver function if clinically indicated
- Virilization in women: voice deepening, clitoromegaly, menstrual disturbances — often irreversible if prolonged
- Rare allergic reactions: rash, pruritus, hypersensitivity
Serious but rare
- Significant liver injury (very rare)
- Thromboembolic events (reported with androgens in general)
- Significant psychiatric effects (severe aggression, mania, depression)
- Marked adverse changes in lipids that may increase long-term cardiovascular risk
Contraindications and precautions
- Known or suspected prostate cancer or male breast cancer
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding — contraindicated (risk of virilization of female fetus/infant)
- Severe hepatic dysfunction (use with caution)
- Uncontrolled cardiovascular disease
- Hypersensitivity to mesterolone or formulation excipients
Monitoring recommendations (typical)
- Baseline: clinical assessment, serum testosterone, LH/FSH, PSA (men >40 or with prostate symptoms), lipid profile, liver function tests (LFTs), and a baseline sperm analysis if fertility is a concern.
- Ongoing: clinical review and laboratory monitoring 3–6 monthly initially, then periodically; monitor PSA and digital rectal exam in older men; lipid profile and LFTs periodically; semen analysis if fertility desired.
Drug interactions (examples)
- Anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin): androgens may potentiate anticoagulant effects — monitor INR and adjust dose as needed.
- Insulin and antidiabetic agents: alterations in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity may occur — monitor glycemic control closely.
- Concomitant hepatotoxic drugs: use caution and monitor liver function.
5. Storage — How to store it
- Store at room temperature, typically 20–25 °C (68–77 °F); brief excursions permissible up to 30 °C (86 °F) unless the product label specifies otherwise.
- Keep tablets in their original container, protected from moisture and light.
- Keep out of reach of children and pets.
- Do not use beyond the expiration date printed on the package.
- Dispose of unused medication according to local regulations or take-back programs; do not flush medications unless directed.
Final notes
- Mesterolone (Proviron) is an androgenic medication with specific clinical uses; therapy should be initiated and supervised by an appropriate healthcare professional.
- Benefits, risks, and monitoring requirements should be discussed with the patient before starting treatment. If you need references, prescribing information, or a sample monitoring schedule, tell me which you prefer and I can provide them.
1. Description — Clinical summary
Proviron is a brand name for mesterolone, an orally active androgenic steroid (a 1α‑methyl derivative of dihydrotestosterone). It is used in some countries for treatment of male androgen deficiency symptoms (e.g., decreased libido, erectile dysfunction related to low androgenic tone), as an adjunct in certain cases of male infertility, and historically for miscellaneous androgen-responsive disorders. Compared with testosterone esters, mesterolone has relatively weak anabolic effects, strong androgen receptor affinity, and does not undergo aromatization to estrogens. It is available as oral tablets (commonly 25 mg).
Indications (typical, depending on local regulatory approval)
- Male hypogonadism or symptomatic androgen deficiency (adjunctive therapy).
- Selective cases of male sexual dysfunction or decreased libido associated with low androgen tone.
- Adjunctive use in some protocols for male infertility (evidence limited and variable).
Contraindications
- Known prostate or breast cancer in men.
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding (risk of fetal virilization).
- Significant hypercalcemia, severe cardiac, hepatic or renal disease may preclude use or require caution.
- Hypersensitivity to mesterolone or excipients.
2. How does proviron work? — Mechanism of action
- Receptor action: Mesterolone is a potent agonist of the androgen receptor (AR). It binds AR in androgen‑sensitive tissues (prostate, seminal vesicles, skin, hair follicles, muscle), producing androgenic effects such as maintenance of male secondary sexual characteristics and influence on libido and sexual function.
- Metabolism and estrogenicity: Mesterolone is a dihydrotestosterone (DHT) derivative and is not aromatized to estradiol; therefore it lacks direct estrogenic effects (no estrogen‑mediated gynecomastia).
- Hypothalamic–pituitary–testicular (HPT) axis: As an androgen it can exert negative feedback on the HPT axis. At typical therapeutic doses this suppression may be minimal, variable, or clinically insignificant in some patients, but higher doses or prolonged use can suppress LH/FSH and impair spermatogenesis.
- Pharmacokinetics (summary): Orally active, metabolized in the liver with renal excretion of metabolites. (Specific absorption and half‑life parameters vary with formulation and individual factors.)
3. Dosage — Medical and varying usage guidelines
General principles
- Dosages below are for informational/educational purposes only. Prescribing should be individualized and directed by a qualified clinician with appropriate baseline assessment and ongoing monitoring.
- Tablet strength is commonly 25 mg. Divide daily dose to maintain steady levels (e.g., morning and evening).
- Reassess response and safety at regular intervals (often 4–12 weeks after initiation).
Typical therapeutic ranges (adult males)
- Androgen deficiency / decreased libido / erectile dysfunction adjunct: 25–50 mg per day, commonly given as 25 mg twice daily or 25 mg morning and 25 mg evening. Some clinicians use 50 mg once daily; multiple daily dosing may maintain steadier levels.
- Male infertility (adjunctive use): 25–50 mg per day if used; evidence for efficacy is limited and effect on fertility is inconsistent. Careful monitoring of semen parameters and gonadotropins is required.
Duration of therapy
- Symptomatic improvements may be noticed over weeks; full clinical assessment may take several months. Duration varies by indication; chronic replacement may be considered only when clinically indicated and monitored.
Special populations and cautions
- Women: Mesterolone is generally contraindicated in women because of strong virilizing potential (hirsutism, voice deepening). If ever used off‑label, extremely low doses have been reported historically, but routine use is not recommended.
- Children/adolescents: Not recommended except under specialist supervision for clearly defined indications due to effects on growth and virilization.
- Elderly: Use caution; start at lower doses and monitor prostate health (PSA) and hematocrit.
- Hepatic/renal impairment: Use cautiously; mesterolone is hepatically metabolized — severe hepatic impairment is a concern.
- Interaction considerations: Androgens may interact with oral anticoagulants (alter INR), insulin and oral hypoglycemics (alter glucose tolerance), and other hormone therapies. Review full medication list with prescriber.
Monitoring during therapy (recommended)
- Baseline and periodic: serum testosterone, LH/FSH if fertility a concern, PSA and digital rectal exam in men >40 or with prostate risk factors, liver function tests, fasting lipid profile, hematocrit/hemoglobin, blood pressure.
- Semen analysis if fertility is an objective or if concerns about spermatogenesis arise.
Non‑medical/off‑label use
- Mesterolone has been used off‑label for performance or physique enhancement. Such uses typically involve higher doses and cycles that increase risk of adverse effects, HPT suppression, and long‑term endocrine disturbance. Non‑medical use is discouraged; discuss risks with a clinician.
4. Side effects — Common and rare adverse effects
Common/adverse effects (clinically important)
- Androgenic effects: acne, oily skin, increased facial/body hair, acceleration of androgenic (male pattern) hair loss in predisposed individuals.
- Libido and mood changes: may increase libido in some, but can cause mood swings, irritability, or aggression in others.
- Cardiometabolic: unfavorable changes in lipid profile (reduced HDL cholesterol, possible increased LDL), fluid retention, and possible increases in blood pressure.
- Prostate effects: prostate enlargement or exacerbation of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) symptoms; possible rise in PSA.
- Hematologic: increased red blood cell mass/polycythemia with prolonged use.
- Reproductive: at higher doses or with prolonged use, suppression of LH/FSH and impairment of spermatogenesis (reduced sperm count) which may be reversible after discontinuation but can persist.
- Hepatic: mesterolone is generally considered less hepatotoxic than 17α‑alkylated anabolic steroids, but transient elevations in liver enzymes and rare hepatic adverse events have been reported — monitor liver function during therapy.
Less common/rare but serious
- Severe liver injury (rare) — cholestatic jaundice has been described with some androgens; monitor clinically and by lab testing if symptoms or risk factors present.
- Thromboembolic events (rare) — risk may be increased with androgen use and polycythemia.
- Virilization in women and children — deepening of voice, clitoromegaly, menstrual irregularities; some effects may be irreversible.
- Exacerbation of prostate cancer — avoid in men with known prostate cancer.
If adverse effects occur
- Reassess the need for continued therapy, consider dose reduction or discontinuation, and evaluate with appropriate testing (hematocrit, liver enzymes, PSA, lipids, semen analysis).
5. Storage — How to store it
- Store in original container at room temperature, typically 15–25 °C (59–77 °F) or as specified on the product label. Short excursions (e.g., 15–30 °C) are usually acceptable depending on labeling.
- Protect from excessive heat, moisture, and direct sunlight.
- Keep tightly closed and keep out of reach of children and pets.
- Do not use tablets beyond the expiration date printed on the packaging.
- Dispose of unused medication per local regulations (take‑back programs preferred); do not flush down sink or toilet unless instructed.
General note and clinical responsibility
This guide provides an evidence‑based summary of proviron (mesterolone) for educational purposes. Individual dosing, monitoring, and treatment decisions should be made by a licensed healthcare professional who can evaluate the patient’s clinical context, contraindications and comorbidities. If you or a patient are considering or taking mesterolone, consult a prescriber for personalized assessment and follow‑up.
1. Description — Clinical summary
Proviron is the trade name commonly used for the active compound mesterolone (often colloquially called "proviron"). Mesterolone is an orally active androgenic steroid derived from dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It has been used in some countries to treat certain forms of male hypogonadism, reduced libido associated with low androgen activity, and (historically and off‑label) as an adjunct in some cases of male infertility. Compared with testosterone, mesterolone has relatively weak anabolic effects but significant androgenic activity; it is not aromatized to estrogens.
Availability and regulatory approval vary by country. Prescribing and monitoring should follow local regulatory guidance and specialist advice.
Important clinical points
- Primary therapeutic uses: symptomatic androgen deficiency in men (when appropriate) and selected off‑label uses in male reproductive disorders. Evidence for fertility benefits is mixed and specialist assessment is recommended.
- Not indicated for use in pregnant or breastfeeding women; contraindicated in people with known prostate cancer or breast cancer in males.
- Androgenic effects and metabolic effects (lipids, hematocrit, prostate) require monitoring.
2. How does proviron work? — Mechanism of action
- Androgen receptor agonist: Mesterolone binds to and activates androgen receptors in androgen‑sensitive tissues (e.g., prostate, skin, muscle, central nervous system), producing androgenic effects (libido, male secondary sex characteristics) and modest anabolic effects.
- DHT derivative and non‑aromatizable: As a DHT derivative, mesterolone is not converted to estradiol by aromatase. Therefore it typically does not produce estrogen‑mediated adverse effects (gynecomastia, fluid retention).
- SHBG binding: Mesterolone has affinity for sex hormone‑binding globulin (SHBG). By competing for SHBG, it can increase the proportion of free (bioavailable) testosterone in plasma, which may contribute to symptomatic improvement in some men with low free testosterone despite normal total testosterone.
- Hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis effects: At higher doses or with prolonged use, androgens (including mesterolone) can suppress LH/FSH secretion via negative feedback, potentially reducing endogenous testosterone production and sperm production.
3. Dosage — Medical and usage guidelines
Note: Dosing should be individualized. The following are general ranges used clinically in adults; follow local product labeling and specialist recommendations.
General adult male dosing (typical therapeutic ranges)
- Usual starting dose: 25 mg two to three times daily (total 50–75 mg/day).
- Typical maintenance range: 25–50 mg two times daily (50–100 mg/day) depending on response and tolerability.
- Administration: oral tablets, usually divided doses (morning and evening) because of relatively short duration of action.
- Duration: based on the treated condition and response; reassess benefit and adverse effects regularly. Long‑term use warrants routine monitoring.
Specific clinical considerations
- Hypogonadism: Mesterolone may be used when androgen replacement is indicated and selection of agent is appropriate. However, standard testosterone replacement (in forms and doses approved in your jurisdiction) is generally preferred when systemic testosterone replacement is required.
- Male infertility/low libido: Doses used in fertility practice have commonly been 25–50 mg/day; evidence for benefit is variable and specialist evaluation (endocrine/reproductive) is recommended prior to therapy.
- Women: Generally not recommended because of the risk of virilization (hirsutism, voice deepening, clitoromegaly). If ever considered (rare, and only under specialist supervision), doses would be very low and the risk of irreversible virilization must be emphasized.
- Children/adolescents: Use is generally contraindicated except under strict specialist supervision for specific, well‑defined indications (e.g., certain disorders of puberty) because of risk of premature epiphyseal closure and virilization.
Special precautions
- Patients trying to conceive: Because androgens can suppress spermatogenesis at higher doses, mesterolone use for men seeking fertility should be managed by a reproductive specialist; it is sometimes used in fertility protocols but may be counterproductive in some cases.
- Athletes: Mesterolone is an androgenic steroid and is prohibited in competitive sport by most anti‑doping authorities. Do not use for performance enhancement.
4. Side effects — common and rare adverse effects
Common and expected effects
- Androgenic/skin: Increased acne, oily skin, exacerbation of androgenetic alopecia (male pattern hair loss).
- Sexual effects: Increased libido in some men; changes in sexual function may occur.
- Hematologic: Increased hematocrit and hemoglobin (erythropoiesis) — monitor for polycythemia.
- Lipid effects: Adverse changes in serum lipids (reduced HDL cholesterol, possible increase in LDL cholesterol), which can increase cardiovascular risk over time.
- Mood/behavior: Mood swings, irritability, aggression or changes in mood in some patients.
Less common but serious or important effects
- HPG axis suppression: With higher doses or prolonged use, suppression of LH/FSH and impaired spermatogenesis, reduced testicular volume and infertility may occur.
- Prostate effects: Exacerbation of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), urinary symptoms, and potential elevation in prostate‑specific antigen (PSA); contraindicated in known prostate cancer.
- Liver effects: Mesterolone is an orally active androgen and is metabolized hepatically. Clinically significant hepatotoxicity is less common than with some 17‑alpha‑alkylated steroids but liver enzyme elevations, cholestasis, and other hepatic adverse events have been reported; monitor liver function in at‑risk patients or with prolonged use.
- Virilization in females and children: Hirsutism, voice deepening, menstrual disturbances, clitoral enlargement (may be irreversible).
- Cardiovascular: Hypertension and increased thrombotic risk have been reported with androgens; long‑term use may increase cardiovascular risk through lipid and other metabolic effects.
- Hypersensitivity: Allergic reactions are possible but uncommon.
When to stop and seek urgent care
- Jaundice, dark urine, severe abdominal pain, or markedly abnormal liver tests.
- Sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, leg swelling or pain (possible thromboembolism).
- New or rapidly worsening urinary symptoms, difficulty urinating, or signs suggestive of prostate disease.
- Signs of severe allergic reaction (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing).
Drug interactions and monitoring
- Anticoagulants: Androgens can potentiate the effect of oral anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), requiring monitoring and dose adjustment.
- Hypoglycemic agents: Androgens can alter glucose metabolism; monitor blood glucose in diabetic patients.
- Other hepatically metabolized drugs: Use caution and review potential interactions.
Monitoring recommendations (typical)
- Baseline and periodic: liver function tests, fasting lipid panel, hematocrit/hemoglobin, testosterone/LH/FSH, PSA in men (especially >40 years), and clinical assessment of benefit and adverse effects. Frequency depends on dose, duration, and patient risk factors.
5. Storage — how to store it
- Keep in the original container with the label intact.
- Store at controlled room temperature, typically 15–30 °C (59–86 °F) or as specified on the product leaflet; avoid extremes of heat and cold.
- Protect from moisture and direct sunlight. Keep the container tightly closed when not in use.
- Keep out of reach and sight of children and pets.
- Do not use tablets past the expiration date on the package. Dispose of unused medication according to local regulations or return to a pharmacy take‑back program.
Final notes
- Prescribe and use mesterolone only under medical supervision. Baseline assessment and regular monitoring help maximize benefit and limit risks.
- Discuss fertility intentions, cardiovascular risk factors, liver disease, prostate disease, and potential for virilization (in women/children) with the prescriber before starting therapy.
- Availability, approved indications, and regulatory status of Proviron/mesterolone vary by country; follow local prescribing information and specialty guidance.
1. Description: Clinical summary
Proviron (generic name: mesterolone, often marketed under the brand name Proviron) is an orally active androgenic steroid derived from dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It is used medically in some countries to treat male hypogonadism, certain cases of infertility associated with low androgen levels, and related androgen-deficiency symptoms (low libido, fatigue, depressed mood when attributable to androgen deficiency). Proviron is a relatively weak anabolic agent but has pronounced androgenic properties and does not undergo aromatization to estrogens.
It is not a first‑line replacement for all forms of testosterone deficiency in many guidelines, and availability/approved indications vary by country. Use should be guided and monitored by a qualified clinician.
2. How does proviron work?: Mechanism of action
- Proviron (mesterolone) is a synthetic androgen that is structurally a DHT derivative (1α‑methyl‑5α‑dihydrotestosterone).
- It binds to the androgen receptor (AR) and activates androgenic signaling in target tissues (prostate, skin, muscle, brain), producing typical androgenic effects (virilization, increased libido, changes in secondary sexual characteristics).
- It does not aromatize to estradiol, so it does not directly increase estrogen levels or cause estrogen‑mediated side effects such as gynecomastia or water retention.
- Mesterolone has high affinity for sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) and can displace endogenous testosterone from SHBG, transiently increasing the fraction of free (bioavailable) testosterone in serum.
- With systemic androgen exposure, negative feedback on the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis can occur, potentially reducing luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle‑stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion and thereby decreasing endogenous testicular testosterone production and spermatogenesis at sufficiently high or prolonged doses.
- Metabolism is hepatic; it is not 17α‑alkylated (unlike many orally active anabolic steroids), so classical 17α‑alkylation–related hepatotoxicity is less pronounced, though hepatic adverse effects are still possible.
3. Dosage: Medical and varying usage guidelines
Important: Dosing should be individualized and prescribed/monitored by a physician. The following are general, literature‑based medical ranges and clinical considerations rather than prescriptive instructions.
-
Formulation and usual tablet strength:
- Commonly supplied as 25 mg oral tablets.
-
Typical adult male medical dosing:
- Hypogonadism/androgen deficiency: commonly 25–50 mg per day in divided doses (e.g., 25 mg twice daily). Some older reports describe total daily doses up to 100 mg in selected cases under supervision.
- Infertility/adjuncts for certain spermatogenic disorders: low to moderate doses (e.g., 25–50 mg/day) have been used as an adjunct in selected patients; treatment courses are usually several months with periodic reassessment of semen parameters and hormonal profile.
-
Elderly patients:
- If used, start at lower end of dosing range and monitor closely for cardiovascular, prostate, and hematologic adverse effects.
-
Women and children:
- Generally contraindicated in women of childbearing potential (risk of virilization) and children (risk of premature closure of epiphyses and virilization). If ever considered in women (rare/exceptional cases), doses are very low and risks must be weighed carefully; in practice, use is typically avoided.
-
Duration:
- Depends on indication. For hypogonadism, replacement may be long‑term with periodic monitoring. For infertility, therapeutic trials often last several months (e.g., 3–6 months) to allow spermatogenic response, with reassessment.
-
Monitoring:
- Baseline and periodic evaluation of serum total and free testosterone, LH/FSH, complete blood count (hematocrit/hemoglobin), liver function tests, lipid profile (HDL/LDL), PSA (in older men) and semen analysis when used for infertility. Monitor blood pressure and signs/symptoms of androgen excess or virilization.
-
Off‑label/performance‑enhancement use:
- Use for athletic performance or bodybuilding is not a medical indication, is often illegal in many jurisdictions, and carries increased risk of adverse effects (HPG suppression, cardiovascular and metabolic harms). This guide does not recommend or provide regimens for non‑medical use.
4. Side effects: Common and rare bad effects
Side effects depend on dose, duration, patient sex, age and comorbidities.
Common/adverse effects
- Androgenic:
- Acne, oily skin, increased seborrhea, male pattern hair loss (androgenic alopecia) in predisposed individuals.
- Increased body/facial hair, voice deepening and clitoral enlargement in females (virilization) — often irreversible if prolonged.
- Endocrine/Hormonal:
- Suppression of endogenous testosterone production and spermatogenesis at sufficient doses/duration (may cause reduced testicular volume and infertility).
- Lipid and metabolic:
- Adverse lipid changes (reduction in HDL cholesterol, possible increase in LDL), which can increase cardiovascular risk over time.
- Psychiatric/behavioral:
- Mood changes, irritability, aggression, changes in libido (may be increased or decreased depending on baseline state and dosing).
- Laboratory:
- Possible increases in hematocrit/hemoglobin (polycythemia), requiring monitoring.
Less common/rare but serious
- Hepatic:
- Hepatotoxicity is less common than with 17α‑alkylated steroids but hepatic dysfunction, cholestasis and abnormal liver tests have been reported; monitor liver function when indicated.
- Cardiovascular:
- Hypertension, potential increased risk of cardiovascular events in susceptible individuals due to lipid and hematologic changes.
- Prostate:
- Aggravation or acceleration of prostate disorders (benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer) or increase in PSA in susceptible men — contraindicated in known prostate carcinoma.
- Hypersensitivity:
- Allergic reactions are rare but possible.
- Female-specific:
- Virilization (hirutism, deepening voice, clitoral enlargement), menstrual irregularities; often contraindicated in pregnancy (can masculinize a male fetus).
Contraindications (select)
- Known or suspected prostate carcinoma or male breast carcinoma.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Known hypersensitivity to mesterolone.
- Caution in patients with severe cardiac, hepatic or renal disease.
Drug interactions (select)
- May interact with oral anticoagulants (monitor INR/bleeding risk).
- Potential interactions with agents influencing lipid metabolism or hepatic enzyme activity — clinical monitoring recommended.
- Inform prescribers of concomitant medications; monitoring and dose adjustments may be necessary.
If adverse effects occur or lab abnormalities develop, consult the prescribing clinician promptly.
5. Storage: HOW to store it
- Store Proviron (mesterolone tablets) at controlled room temperature, typically between 15°C and 25°C (59°F–77°F), unless the product labeling specifies otherwise.
- Protect from excessive heat, moisture and direct sunlight. Keep the tablets in their original container/blister until use to protect from light and humidity.
- Keep out of reach of children and pets.
- Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package.
- Dispose of unused or expired medication according to local regulations or pharmacy guidance; do not flush medications down the toilet unless instructed.
General clinical note
- Proviron is a prescription medication. Initiation and continuation should be based on a clinical diagnosis and under physician supervision with appropriate baseline and periodic monitoring (hormones, lipids, hematocrit, liver function, prostate assessment in older men). Because of its androgenic effects and potential for endocrine disruption and cardiometabolic harm, unsupervised or non‑medical use is discouraged.
1. Description — Clinical summary
Proviron is a brand name for mesterolone, an orally active synthetic androgen and a derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It has been used clinically in some countries for treatment of male hypogonadism, decreased libido related to androgen deficiency, and historically as an adjunct in some infertility regimens. Compared with other androgens, mesterolone has relatively weak anabolic activity and strong androgenic potency; it does not aromatize to estrogens. Its indications, availability and authorized dosing vary by country. Use should be by prescription and under medical supervision.
Key clinical points
- Active compound: mesterolone (an androgen, DHT derivative).
- Main intended use: treatment of symptoms of androgen deficiency in males (e.g., low libido, some features of hypogonadism); historically used in some fertility protocols.
- Not an estrogenic agent and does not convert to estradiol (so gynecomastia risk from aromatization is low).
- Use requires physician oversight because of androgenic, metabolic and cardiovascular effects.
2. How does proviron work? — Mechanism of action
- Mesterolone is an agonist at the androgen receptor (AR). It binds AR in target tissues (muscle, prostate, skin, brain, etc.) and activates androgen-responsive gene expression.
- It is a DHT derivative and therefore is not a substrate for the aromatase enzyme; it does not convert to estrogenic metabolites.
- It has relatively low anabolic (protein-building) activity compared with testosterone esters and other anabolic steroids, but retains marked androgenic effects (e.g., on libido, male secondary sexual characteristics).
- By providing androgen receptor stimulation, mesterolone exerts negative feedback on the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis and can suppress endogenous luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), especially with higher doses or prolonged use. This can impair spermatogenesis in some settings.
- There are reports that mesterolone may bind to sex-hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) and thereby increase free (bioavailable) testosterone, but the clinical significance of this is variable.
3. Dosage — Medical and usage guidelines
General principles
- Mesterolone dosing must be individualized, based on the indication, severity of deficiency, patient age, comorbidities and laboratory monitoring. Always follow local prescribing information and the supervising clinician’s plan.
- Do not use without prescription. Avoid off-label or non-medical use (e.g., for bodybuilding) because of health risks.
Typical clinical dosing (historical/commonly reported ranges)
- Adult males with androgen deficiency or decreased libido: commonly 25–50 mg per day, often given as 25 mg twice daily or 25 mg three times daily. Some practitioners have used up to 100 mg/day in divided doses, but higher doses increase risk of adverse effects and are not routinely recommended.
- Male infertility: historically 25–50 mg/day for several months has been used in certain protocols, but high-quality evidence for improved fertility is limited; specialist oversight (andrologist/urologist) is advised.
- Use in women: generally not recommended because of virilizing (masculinizing) effects. If ever used (rare and exceptional), doses are very low and subject to specialist guidance; pregnancy and lactation are contraindications.
- Duration: depends on indication. For symptom relief in hypogonadism, therapy may be long-term under monitoring; for infertility trials, treatment courses are typically months with periodic reassessment of semen parameters. Discontinue if no benefit or if adverse effects develop.
Dose adjustments and special populations
- Elderly patients and those with cardiovascular disease, prostate disease, hepatic impairment or significant comorbidities: start at the lowest effective dose and monitor closely.
- Children and adolescents: use is generally contraindicated except under strict specialist guidance for specific conditions; exogenous androgens can accelerate epiphyseal closure and disrupt normal development.
Monitoring during therapy
- Baseline: physical exam (including prostate exam in older men), serum total testosterone, LH, FSH, PSA (if age-appropriate or risk factors), liver function tests (LFTs), fasting lipid panel, hematocrit/hemoglobin, and semen analysis if fertility is a concern.
- Follow-up: reassess symptoms and repeat labs periodically (for many patients every 3 months initially, then every 6–12 months); check PSA and prostate status in men at risk; monitor LFTs and lipids as clinically indicated. Adjust or stop therapy if adverse trends occur.
Important cautions
- Contraindicated in men with known or suspected prostate or breast cancer.
- Use with caution in patients with cardiovascular disease, hyperlipidemia, sleep apnea, polycythemia, or significant hepatic impairment.
- If planning conception, discuss fertility implications with your clinician; androgens can adversely affect spermatogenesis in some cases.
4. Side effects — Common and rare adverse effects
Common or probable adverse effects
- Androgenic effects: acne, oily skin, increased facial/body hair, acceleration of male pattern baldness in genetically predisposed men.
- Prostate effects: increased prostate size or exacerbation of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) symptoms; potential to worsen undiagnosed prostate cancer.
- Reproductive axis effects: suppression of endogenous LH/FSH with possible changes in spermatogenesis (variable).
- Metabolic effects: unfavorable changes in lipid profile (decrease in HDL cholesterol, increase in LDL cholesterol) which may raise cardiovascular risk over time.
- Hematologic: increased hematocrit/polycythemia in some patients, which can increase thrombotic risk.
- Psychological/behavioral: mood changes, increased irritability or aggression in susceptible individuals.
Less common or rare but serious effects
- Hepatic effects: although mesterolone is not a classical 17α‑alkylated steroid, cases of liver enzyme abnormalities and cholestatic liver injury have been reported with oral androgens; monitor LFTs if clinically indicated.
- Cardiovascular events: exacerbation of hypertension, increased risk of ischemic events in high-risk patients over long-term use (related to lipid changes and other androgen effects).
- Venous thromboembolism (rare) possibly related to polycythemia or other prothrombotic changes.
- Virilization in women and children: deepening of voice, clitoromegaly, menstrual irregularities—these may be irreversible if exposure prolonged.
- Hypersensitivity reactions (rare).
What to do if side effects appear
- Mild side effects: report to prescribing clinician; dose adjustment or symptomatic treatment may be possible.
- Serious or progressive symptoms (jaundice, marked LFT elevations, chest pain, stroke symptoms, significant polycythemia, severe prostate symptoms, severe mood/behavioral changes): stop the drug and seek immediate medical attention.
- For women who are pregnant or suspect pregnancy: mesterolone is contraindicated because of risk of virilization of a female fetus.
5. Storage — How to store it
- Store oral mesterolone tablets at room temperature, generally between 20–25°C (68–77°F), unless the product labeling specifies otherwise. Short excursions outside this range are usually acceptable, but avoid extremes of heat or cold.
- Keep the medication in its original container, tightly closed, and protected from moisture and light as per the product leaflet. Do not store in bathroom or other humid places.
- Keep out of reach of children and pets.
- Check the manufacturer’s or dispenser’s labeled expiration date; do not use beyond the expiry.
- Dispose of unused or expired medication according to local regulations—return to a pharmacy take-back program if available; do not flush medications down the toilet unless instructed.
Additional practical and safety notes
- Always take mesterolone exactly as prescribed; do not change dose or stop abruptly without discussing with the prescriber.
- Inform your clinician about all other medications, supplements and medical conditions (particularly prostate/breast disorders, cardiovascular disease, liver disease, sleep apnea, and planned fertility/pregnancy).
- Regular follow-up and laboratory monitoring are important to balance potential benefits against known risks.
If you want, I can provide a printable quick-reference sheet with typical baseline and follow-up labs, contraindications, and red-flag symptoms to watch for.